VetStat
General
The
Danish VetStat database was established in 2000. It is owned and managed by the
Danish Veterinary and Food Administration agency of the Ministry of Environment
and Food of Denmark. VetStat was among the first data collection systems to
become operational in retrieving detailed data on sales of prescribed drug for
animals, hence product packages specific. Data comprises all animals, although
the detailing level of production animals is considerably higher, with data at farm
level, than the equivalent data for horses and pets.
Data collection
Sub-categories of
animal species: of
pigs: breeding animals (sows, boars, gilts and sucklers), weaners (< 30 kg) and
finishers; of cattle: cows, bulls, heifers and steers > 24 months, calves
< 12 months and youngster between 12 and 24 months; of sheep/goats: animals
< or > 12 months; and of poultry: broilers, layers and breeding stock.
Input: Pharmacies and feed-mills are obliged to report sold amount of drugs for all animal species, while vets report the amount of drugs used for production animals in veterinary practice. Livestock owners do not provide data, however, they are obliged to register the specific usage of prescribed drugs and store these registrations for five years in the farm. For standardization of antimicrobial usage at farm level, the needed number of animals can be obtained from the Central Husbandry Register and represent average capacity numbers.
Input: Pharmacies and feed-mills are obliged to report sold amount of drugs for all animal species, while vets report the amount of drugs used for production animals in veterinary practice. Livestock owners do not provide data, however, they are obliged to register the specific usage of prescribed drugs and store these registrations for five years in the farm. For standardization of antimicrobial usage at farm level, the needed number of animals can be obtained from the Central Husbandry Register and represent average capacity numbers.
Analysis
The
dose-based unit of measurement ADD (animal daily dose; defined per product at
the active substance level) is used to calculate the indicator ADD per 100
animals per day. Recently, weighted ADD values have been established, in order
to discourage the use of certain types of antimicrobials and encourage the use
of others. The kg animal at risk of treatment is determined using standard
weights defined nationally. The use for companion animals is calculated based
on the sales of veterinarian products from pharmacies to veterinarians.
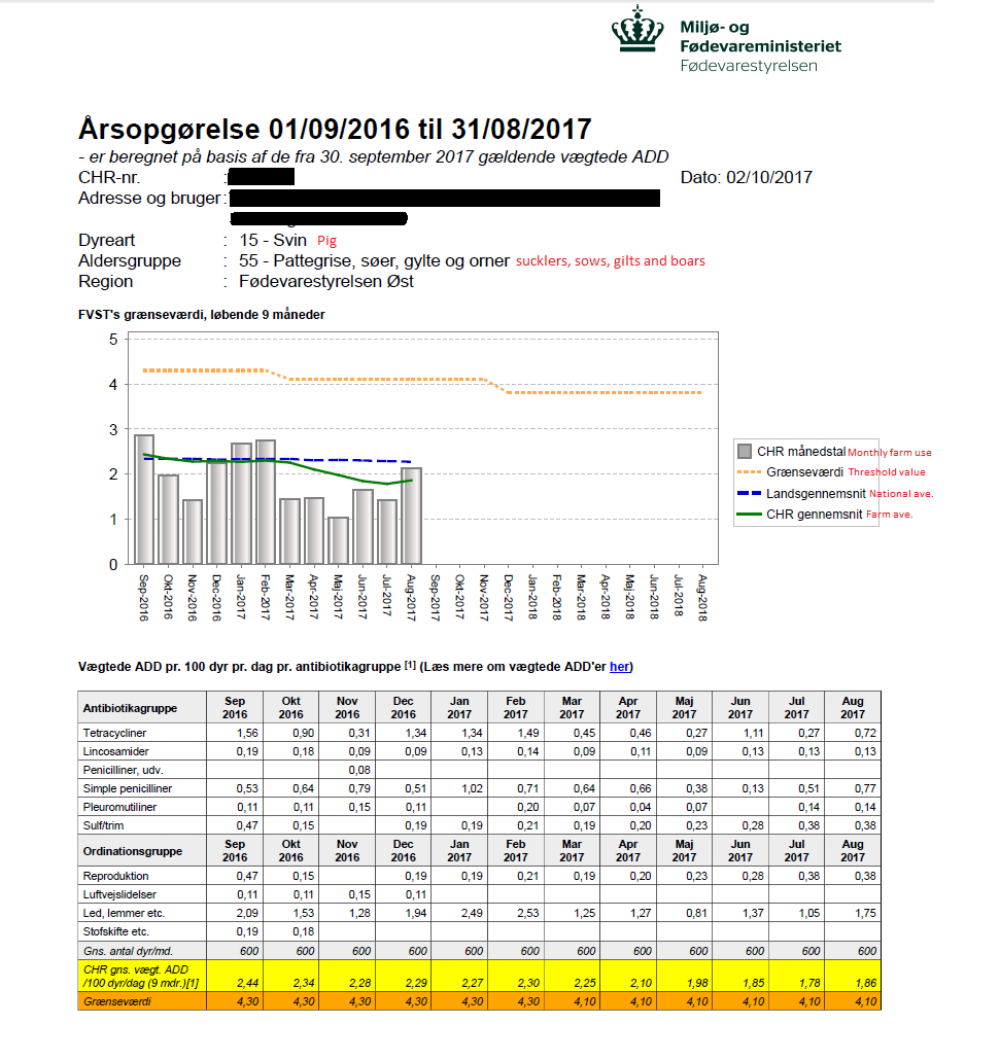
Benchmarking
Benchmarking
is currently applied to pigs and cattle. One threshold value is defined per
weight category, above which the average ADD/100 animals/day calculated over
the last nine months (time frame) may not pass to prevent inhibitory measures
becoming in force. This is for pigs referred to as the ‘yellow card initiative’.
For cattle a similar system is in place. In contrast to pigs, no sanctions are
currently in place for cattle, because the threshold values for this species
are a guideline rather than a sanctioning tool. As the system is online
available, farms can follow their position relative to the threshold at any
time – hence, there is no defined frequency for the benchmarking.
Reporting
VetStat
has an interface for vets with graphs and data, as well as an internet based presentation
to farmers. Vets can however apply own benchmarking programmes, the results of
which however are secondary to those of the official methodology and results.